Abstract
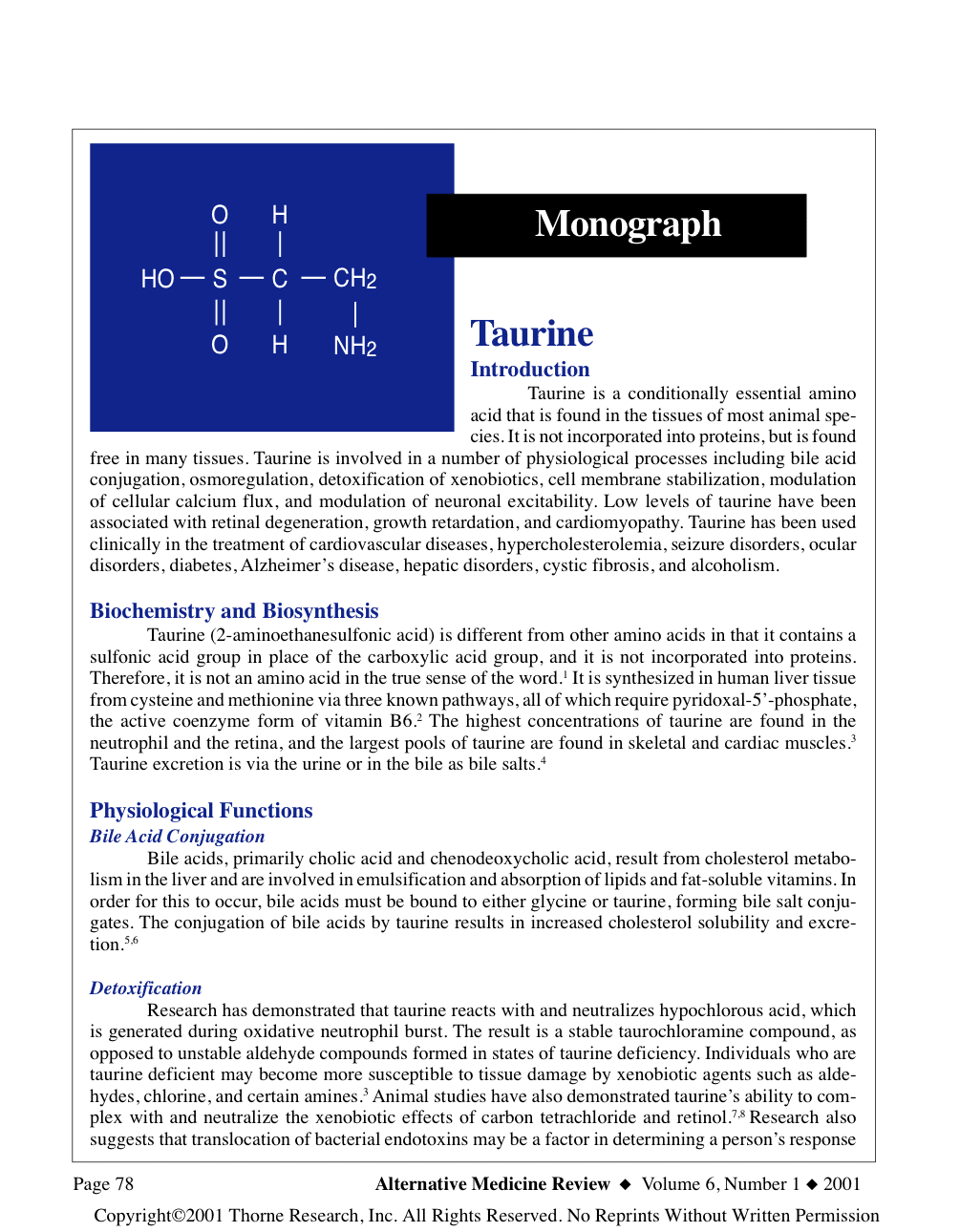
Taurine is a conditionally essential amino acid that is found in the tissues of most animal species. It is not incorporated into proteins, but is found free in many tissues. Taurine is involved in a number of physiological processes including bile acid conjugation, osmoregulation, detoxification of xenobiotics, cell membrane stabilization, modulation of cellular calcium flux, and modulation of neuronal excitability. Low levels of taurine have been associated with retinal degeneration, growth retardation, and cardiomyopathy. Taurine has been used clinically in the treatment of cardiovascular diseases, hypercholesterolemia, seizure disorders, ocular disorders, diabetes, Alzheimer’s disease, hepatic disorders, cystic fibrosis, and alcoholism.